How to Read a Topographical Trail Map? – Everything You Need to Know
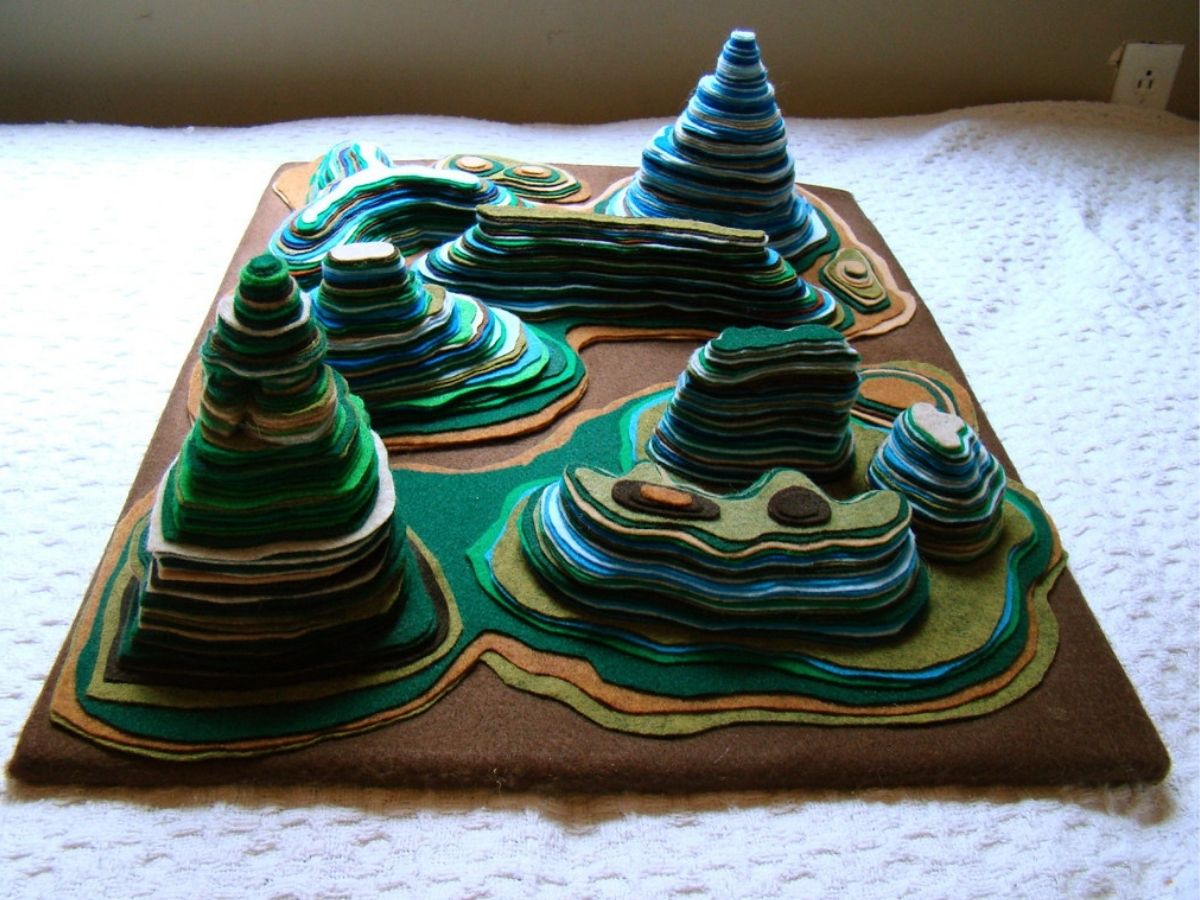

How to read a topographical trail map is a popular question for many hikers and backpackers. A topographical map shows the elevations of mountains, hills, and valleys on a map. The contour lines on a topographical map connect points of equal elevation.
Today, we bring you information and guidelines on how to read a topographical trail map. The benefit of being aware of how to read a topographical map while hiking or backpacking is that you will be able to plan and execute your hike or backpacking trip with greater precision and safety.
What is a Topographic Map?
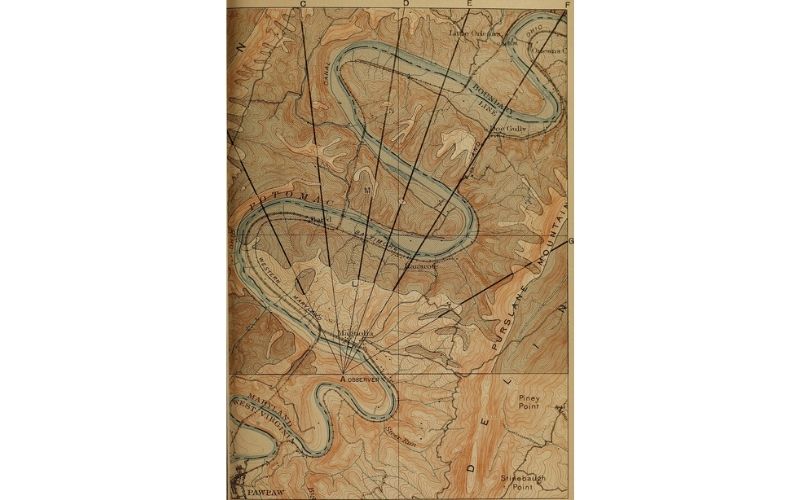
A topographic map shows the elevations of mountains, hills, and valleys on a map. The contour lines on a topographical map connect points of equal elevation. A topographic map is also popular as a contour map.
To explain further, with the use of a topographic map, travelers and backpackers can determine the elevation of any particular point on a map. The map will illustrate all of the features in the surrounding area, including mountains, valleys, rivers, and lakes.
The contour lines on a topographical map will help backpackers and hikers determine areas with steep slopes as well as identify flat areas for camping. Furthermore, topographic maps are very beneficial in determining the amount of water that is available in an area.
Read more: How to use the compass when going to the forest
What Information is on a Topographic Map?
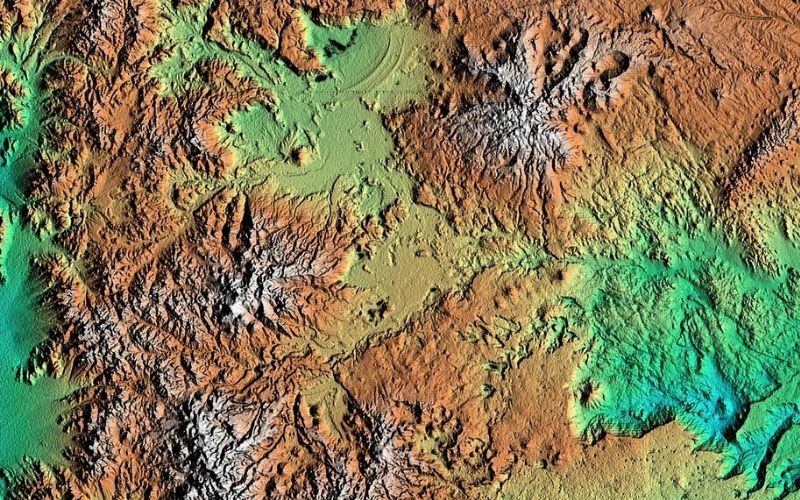
Below are some points on the information that is on a topographic map:
- Relief Features
This means all of the features in the surrounding area, including mountains, valleys, rivers, and lakes. These will allow hikers and backpackers to navigate with greater ease.
- Hydrography
This includes the depiction of water features on a map, such as rivers and streams. Using hydrography one can determine the amount of water available in an area. Moreover, hikers and backpackers can also find water sources on a map by looking for the presence of rivers and streams.
- Vegetation
This information is important for hikers and backpackers as it can indicate the types of vegetation in an area. This will help individuals preparing for a hike or backpacking trip to know what to expect in regards to vegetation.
- Transportation
Knowing where roads and trails are on a map can be helpful for hikers and backpackers. This will allow individuals to plan their route and be aware of any possible transportation obstacles they may encounter on the hike or backpacking trip.
- Culture
A topographic map also includes culture. This can include information such as place names, points of interest, and trail junctions.
- Boundaries
When you know where the boundaries of an area are on a map, it can be helpful for hikers and backpackers. This will allow individuals to know where they can hike or backpack and where they are not.
- Toponymy
With information as points of interest and trail junctions, hikers and backpackers can be familiar with the names of different areas. This will help individuals navigate with greater ease while on a hike or backpacking trip.
Topographical Map Features
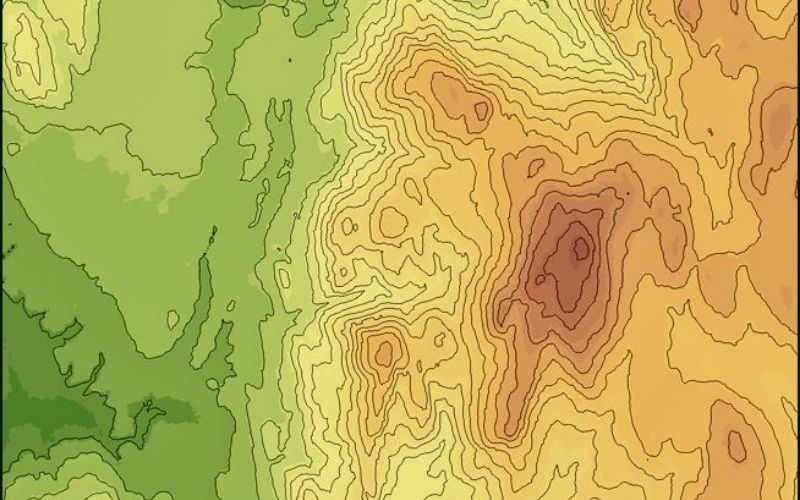
Contour Lines
A contour line on a topographical map connects points of equal elevation. The map reader can use these lines to determine the shape of the terrain by looking at the direction of the contour lines.
Contour Interval
This is the distance between two consecutive contour lines on a map. The contour interval will be on the map and it is important to note that the interval may change depending on the map scale.
Scale
The scale of a map is the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. It is important to be aware of the map’s scale when reading a topographical map as it will affect how accurate the elevation readings are.
Tilthe North Arrow
The tilt of a topographical map is the angle at which the map is projected from the ground. This information is important to take into account when reading a topographical map as it will affect how the elevations are on the map.
Map Legend
The map legend is a key that will explain the different symbols and colors on a topographical map. This is important to reference when trying to decipher information on a topographical map.
How to Read a Topographic Map while on The Trail

Orient Your Map
This method is useful for hikers and backpackers when they are not able to view a map in its entirety. In order to orient your map, you will need to find two or three landmarks on the map. Once you have found these landmarks, line them up on the map with your actual surroundings. This will help you get an idea of where you are located on the map.
Find Your Location on the Map
This method is useful for hikers and backpackers when they can view their map in its entirety. To find your location on the map, you will need to identify at least two landmarks on the map. Once you have found these landmarks, locate them in your actual surroundings. Next, draw a line between the two landmarks and measure the distance. This will give you an idea of how far away you are from these landmarks.
Read the Contour Lines
When reading contour lines, you will need to determine the shape of the terrain by looking at the direction of the contour lines. In addition, you will need to take into account the contour interval as it will affect how accurate the elevation readings are.
Identify the Landscape Features on Your Topographical Map
Landscape features are quite easy to identify on a topographical map. By looking at the shape and direction of the contour lines, you can get an idea of what the feature is. Some common landscape features that are common on a topographical map include mountains, valleys, ridges, and hills.
Lines on the Paper
On a topographical map, the lines on the paper represent trails. By following these lines, hikers and backpackers can navigate their way through the terrain. In addition, these lines will also help individuals identify different points of interest along the trail.
Recognizingizing Terrain Features
These are symbols that are on a topographical map to represent different terrain features. By recognizing these symbols, hikers and backpackers can get an idea of what they will be encountering on their hike or backpacking trip. Some common terrain features on a topographical map include water features, forests, and buildings.
Map Scale
Map scale on a topographical map is the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This information is important to be aware of when reading a topographical map as it will affect how accurate the elevation readings are.
Map Key
The map key is a legend that will explain the different symbols and colors that are on a topographical map. This is important to reference when trying to decipher information on a topographical map.
Pickingractice, Practice, Practice!!!
Practice makes perfect! The more you use topographical maps, the easier it will be for you to read and understand the information on them. So, get out there and start hiking and backpacking! You’ll be a pro in no time!
By following these tips, hikers and backpackers can easily read and understand a topographical map. By understanding the information on a topographical map, individuals will be able to navigate their way through the terrain with ease. In addition, hikers and backpackers will be able to identify different points of interest along the trail.
Useful Tips for Learning How to Read a Topographical Map

Look Closely at The Map Legend
This is an important tip to remember when reading a topographical map. By looking at the map legend, hikers and backpackers can decipher the different symbols and colors on the map. In addition, the map key will explain how to interpret the information on them.
Get Out on The Trail with Your Topographical Map
The best way to learn how to read a topographical map is to practice, practice, practice! By using a topographical map while hiking and backpacking, individuals will be able to familiarize themselves with the different symbols and colors that are on the map. In addition, they will also learn how to interpret the information on the map.
Topographic Terminology

Before reading a topographical map, it is important to understand some of the basic terminologies that are used. This will help you decipher the information that is represented on the map. Some common terms that are used include contour lines, elevation, and land features.
By following these tips, hikers and backpackers can easily read and understand a topographic map.
- Bearing: The direction that you are traveling in relation to a fixed point.
- Classified Roads: Paved roads that are open to the public, but are not accessible by motor vehicle.
- Contour lines: Lines on a topographic map that connect points of equal elevation.
- Elevation: The height of a point relative to a fixed reference point.
- Horizontal Datum: The reference point from which elevations are measured.
- Legend: The key that explains the different symbols and colors that are used on a topographic map.
- Magnetic North: The direction that a compass points.
- Mean Sea Level: The average height of the surface of the ocean.
- National Topographic System: A system of topographic maps that are maintained by the United States Geological Survey.
- Projection: The method by which a three-dimensional object is represented on a two-dimensional surface.
- Relief: The physical features of a landscape.
- Spot Elevation: The height of a point above or below a reference point.
- Symbols: The icons that are used on a topographic map to represent different features in the landscape.
- Topography: The physical features of a landscape.
- Unclassified Roads: Paved roads that are not open to the public.
FAQs Related to “How to Read a Topographical Trail Map?”

How Can I Tell the Difference Between a Hill and a Mountain on a Topographical Map?
On a topographical map, hills are represented by contour lines that are close together, while mountains are represented by contour lines that are further apart. In addition, mountains will usually have a peak or ridge that is represented by a symbol on the map.
Where is the Magnetic North Pole?
The Magnetic North Pole is located in the Arctic Ocean, north of Canada.
How Do I Convert Elevations from Feet to Meters?
To convert elevations from feet to meters, divide the elevation by 3.28. For example, if an elevation is 4500 feet, divide 4500 by 3.28 to get a conversion of 1377 meters.
What is the Mean Sea Level?
The Mean Sea Level is the average height of the surface of the ocean. It is used as a reference point for measuring elevations on a topographic map.
How Does a Topographical Map Work?
A topographical map works by projecting the three-dimensional landscape onto a two-dimensional surface.
Where Can I Find a Topographical Map?
Topographical maps are available from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and other government agencies. They can also be purchased from map retailers.
Is There a Difference Between a Topographical Map and a Satellite Image?
Yes, there is a difference between a topographical map and a satellite image. A topographical map is a map that shows the physical features of a landscape, while a satellite image is a photograph of a landscape taken from space.
Conclusion
After reading these tips and tricks, now you know how to enjoy your winter camping trip with great success! First of all, your winter camping checklist should include all the essential things that you need for camping in the winter. When camping in winter, don’t forget to bring extra clothes and warm blankets with you; it is a must for your winter camping checklist.